Understanding FDM: A Revolutionary Approach in Art Supplies, Product Design, and 3D Printing
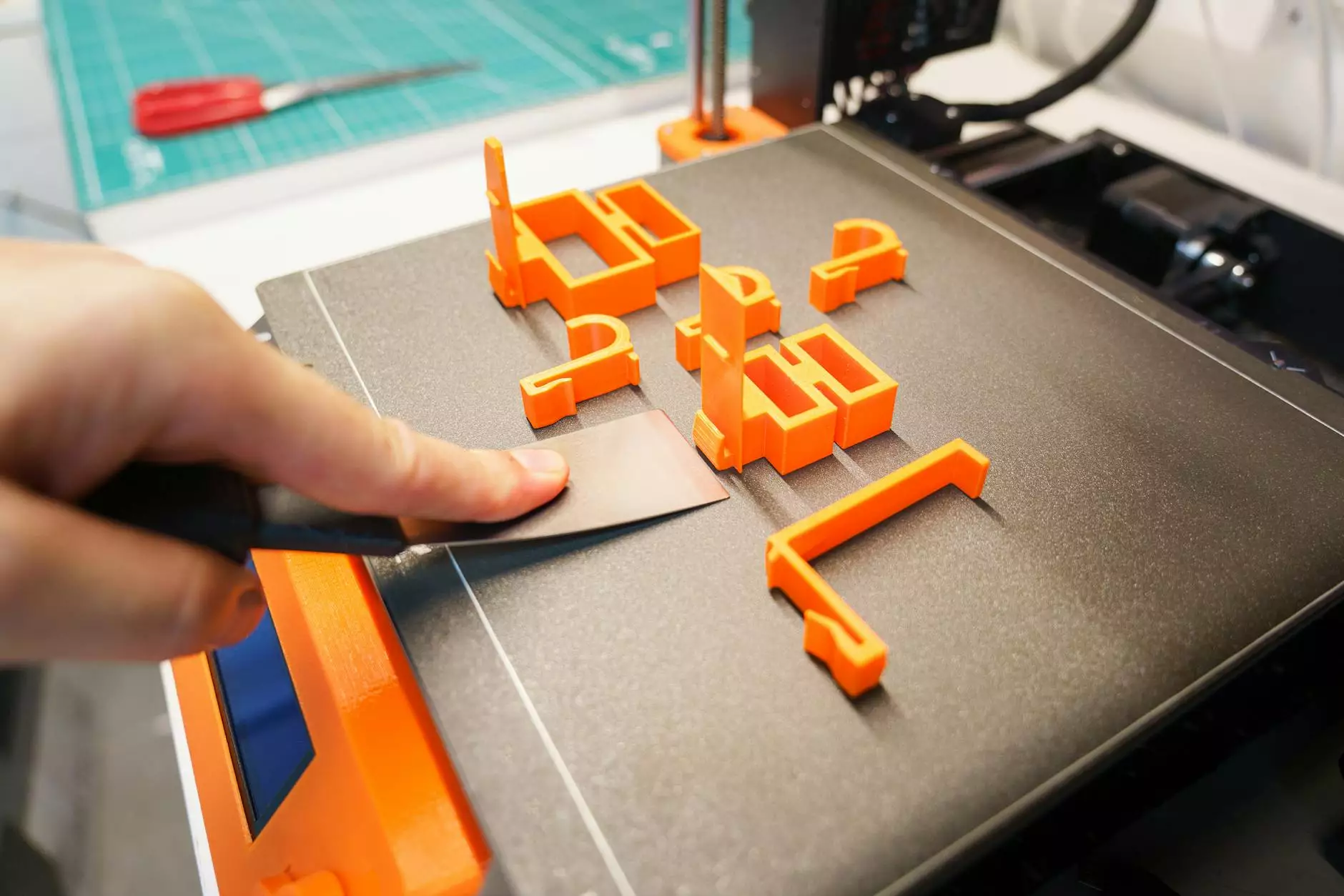
The world of FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) has revolutionized several industries, particularly in art supplies, product design, and 3D printing. This innovative technology allows creators to transform their ideas into tangible products through a straightforward yet effective process. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of FDM, exploring its applications, advantages, and the many ways it enhances creativity in various domains.
What is FDM?
FDM is a type of 3D printing technology where a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle to build a three-dimensional object layer by layer. This method is popular among designers, engineers, and artists alike, primarily for its accessibility and efficiency in producing prototypes and end-use products. The FDM process is characterized by the following steps:
- Model Creation: An initial design is created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
- Slicing: The 3D model is sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software.
- Printing: The printer extrudes the filament in specified patterns to build each layer.
- Post-Processing: Once the object is printed, it may require finishing touches, such as sanding or painting.
Benefits of FDM Technology
The use of FDM offers numerous benefits that make it stand out in the fields of art supplies, product design, and 3D printing:
1. Cost-Effective Production
FDM technology is generally more affordable than other 3D printing methods. The materials used are less expensive, making it an optimal choice for startups and smaller businesses.
2. Wide Range of Materials
FDM supports various types of filament, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and specialty materials such as flexible and composite filaments. This versatility allows artists and designers to experiment with different properties.
3. Ease of Use
FDM printers have a reputation for being user-friendly. Many models come with intuitive software and require minimal setup, making them accessible to beginners in the field of 3D printing.
4. High Precision and Detail
Modern FDM printers can achieve impressive resolutions, allowing for intricate designs and high detail in the final products.
Applications of FDM in Different Industries
The versatility of FDM technology lends itself to a multitude of applications across various industries:
1. Art Supplies
In the realm of art supplies, FDM printers are utilized to create custom tools, sculpture components, and personalized creations. Artists can produce unique pieces that reflect their style, such as:
- Custom stencils and molds for painting and crafting.
- Unique sculptural elements that can be combined with traditional materials.
- Artistic prototypes for projects before full-scale production.
2. Product Design
In product design, FDM technology allows for rapid prototyping, which is crucial for iterative testing and feedback. Product designers can:
- Create and test functional prototypes quickly.
- Visualize concepts in three dimensions.
- Refine designs based on real-world usage scenarios.
3. 3D Printing and Manufacturing
On the manufacturing front, FDM is commonly used to produce low-volume runs of final parts. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods benefit from rapid production times. Key uses include:
- Manufacturing customized parts for machinery.
- Creating replacement parts for older equipment.
- Developing limited edition products that cater to niche markets.
The Future of FDM Technology
The future of FDM technology looks promising as innovations continue to emerge:
1. Advancements in Material Science
Research is ongoing to develop new and improved materials that offer enhanced mechanical properties, sustainability, and greater ease of use.
2. Integration of AI and Automation
Future FDM printers may incorporate AI-driven features that optimize the printing process, ensuring higher quality and reducing errors.
3. Sustainable Practices
As environmental concerns rise, the development of biodegradable and recycled filaments is likely to be a priority within the FDM industry, promoting sustainability without compromising performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FDM technology has significantly impacted art supplies, product design, and 3D printing, providing endless possibilities for creativity and innovation. With its cost-effectiveness, versatility, and user-friendliness, FDM continues to attract enthusiasts, professionals, and businesses alike. As we advance into a future filled with new materials and technology, the potential for FDM to transform the creative landscape is truly exciting.
To learn more about incorporating FDM technology into your projects or to explore an extensive range of art supplies and design tools, visit arti90.com today!